Inductive proximity switches might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, but they’re actually a cornerstone of modern automation. Ever wondered how machines “sense” objects without touching them? That’s where these little marvels come into play. In this article, we’ll dive deep into the world of inductive proximity switches, breaking down what they are, how they work, and why they’re so important. Ready to geek out? Let’s go!
—
What is an Inductive Proximity Switch?
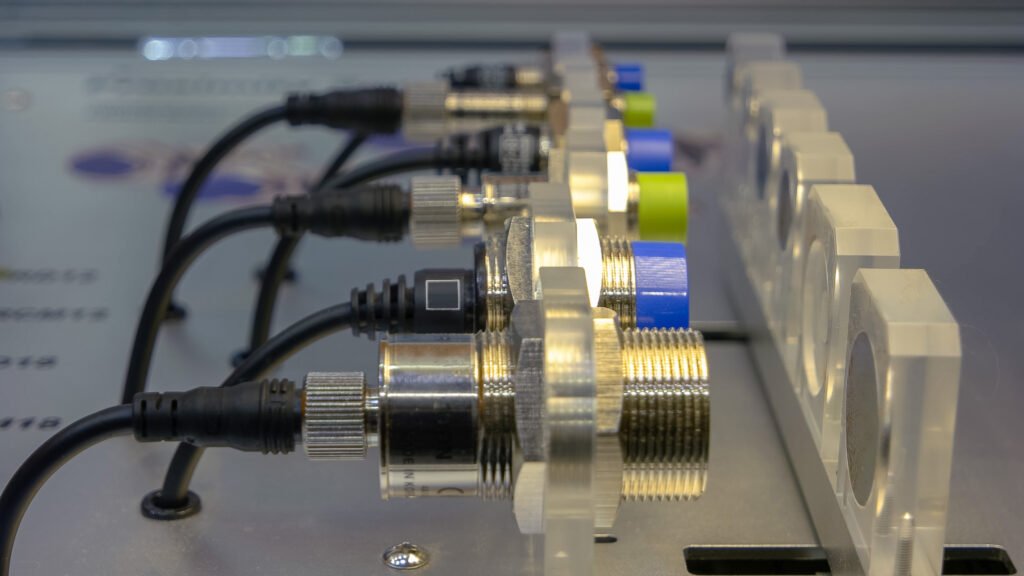
An inductive proximity switch is a non-contact sensor that detects metallic objects without physical interaction. Think of it as a silent guardian that keeps an eye on things—literally. It’s widely used in industrial automation, robotics, and even everyday appliances.
How Does an Inductive Proximity Switch Work?
At its core, an inductive proximity switch uses electromagnetic fields to detect metallic objects. When a metal object enters its sensing range, it disrupts the electromagnetic field, triggering the switch. It’s like a game of hide-and-seek, but with magnets and metal!
The Science Behind It
The switch generates an oscillating magnetic field. When a metal object enters this field, eddy currents are induced in the object, causing a change in the oscillation. This change is detected by the switch, which then sends a signal.
Key Components of an Inductive Proximity Switch
Let’s break it down:
1. Oscillator: Generates the electromagnetic field.
2. Coil: Creates the magnetic field.
3. Detection Circuit: Monitors changes in the field.
4. Output Circuit: Sends the signal when an object is detected.
Types of Inductive Proximity Switches
Not all inductive proximity switches are created equal. Here are the main types:
1. Shielded: Ideal for tight spaces, with a focused sensing range.
2. Unshielded: Offers a wider sensing range but requires more space.
3. High-Temperature: Designed for extreme environments.
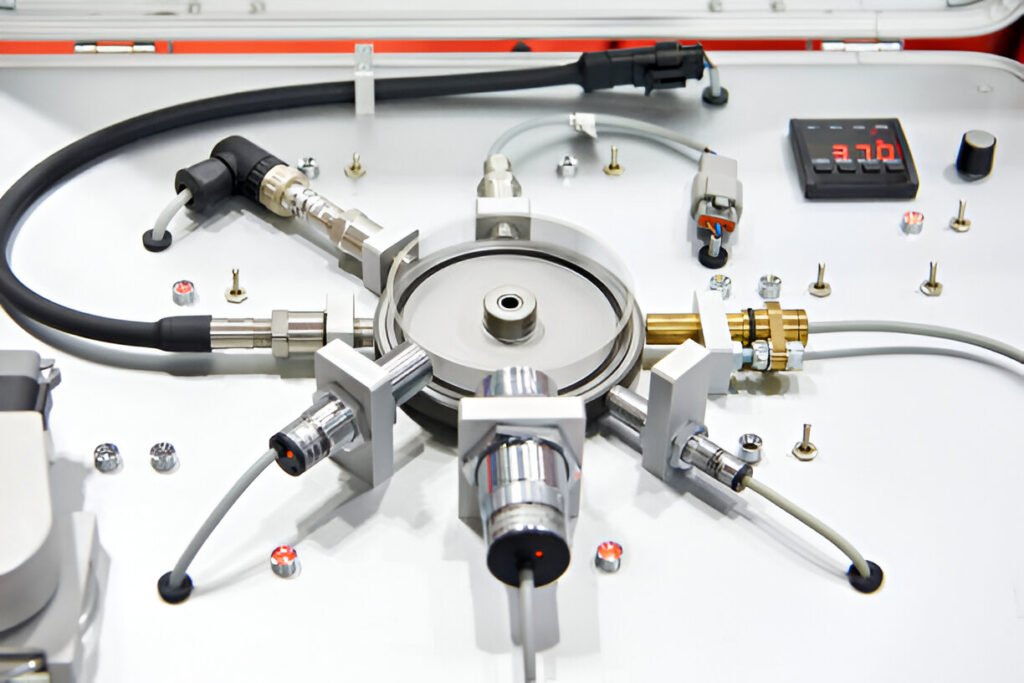
Applications of Inductive Proximity Switches
These switches are everywhere! From conveyor belts in factories to elevators in buildings, they play a crucial role in automation. They’re also used in:
– Automotive assembly lines
– Packaging machinery
– Robotics
– Security systems
Advantages of Using Inductive Proximity Switches
Why are they so popular? Here’s why:
Non-contact operation
High reliability
Fast response time
Limitations of Inductive Proximity Switches
They’re not perfect, though. Here are a few drawbacks:
Limited to metals
Sensing range
How to Choose the Right Inductive Proximity Switch
Picking the right switch can be tricky. Consider:
Sensing range
Environment
Output type
Installation and Maintenance Tips
Installing an inductive proximity switch is straightforward, but here are some tips:
Mount securely
Check alignment
Regular cleaning
Future Trends in Inductive Proximity Switch Technology
The future looks bright! Expect:
Miniaturization
Smart sensors
Enhanced materials
—
Conclusion
Inductive proximity switches are the unsung heroes of automation, quietly making our lives easier. Whether it’s in a factory, a car, or even your home, these devices are everywhere, doing their job with precision and reliability. As technology advances, we can only expect them to get smarter, smaller, and more efficient. So, the next time you see a machine “magically” detect an object, you’ll know the science behind it!
—
FAQs
What materials can inductive proximity switches detect?
Inductive proximity switches can only detect metallic objects, such as steel, aluminum, and copper.
Can inductive proximity switches work underwater?
Yes, some models are designed to work in wet or underwater environments, but always check the IP rating before use.
How long do inductive proximity switches last?
With no moving parts, these switches can last for years, often exceeding 100,000 hours of operation.
Can I use an inductive proximity switch for non-metallic objects?
No, inductive proximity switches are specifically designed for metallic objects. For non-metallic detection, consider capacitive proximity switches.
What’s the difference between shielded and unshielded inductive proximity switches?
Shielded switches have a focused sensing range and are ideal for tight spaces, while unshielded switches offer a wider range but require more installation space.