La magia de los sensores capacitivos: Cómo funcionan y por qué son importantes
En este artículo nos adentraremos en el mundo de los sensores capacitivos y exploraremos sus principios y aplicaciones.
Seguir leyendo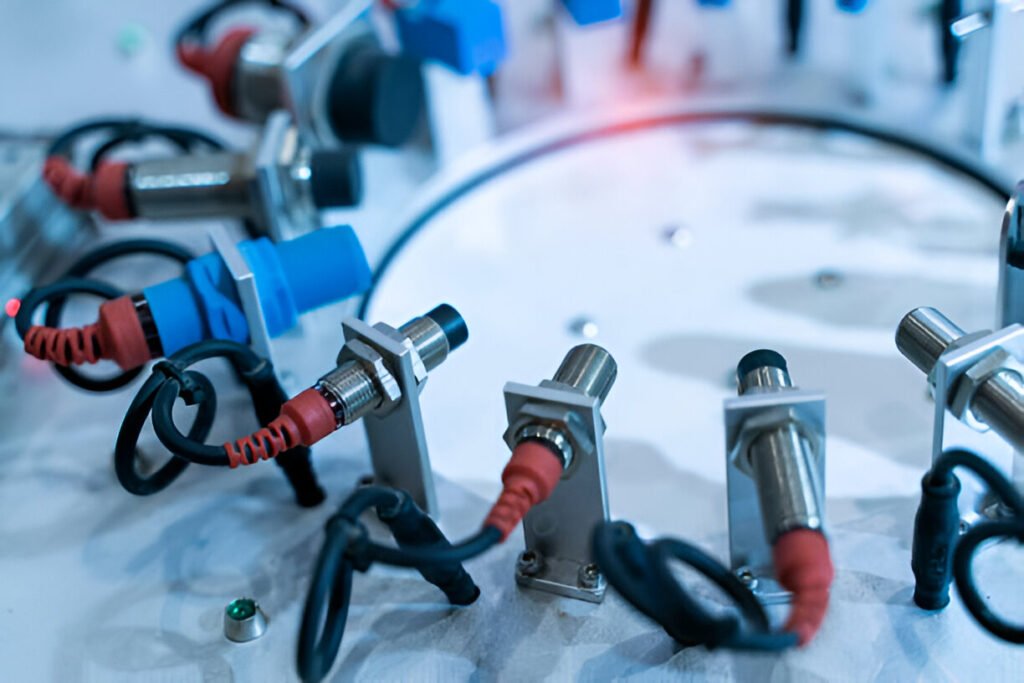

Cuando busque el sensor de proximidades posible que te encuentres con términos técnicos como "tipo de salida", especialmente NPN y PNP. No se preocupe: suenan complicados, pero elegir el tipo de salida correcto es crucial para el funcionamiento de su dispositivo. No sólo afecta a la compatibilidad con el sistema de control, sino también a la estabilidad y seguridad de toda la instalación.
Imagínese que compra un coche, pero el tapón de la gasolina no encaja: la experiencia no sería muy buena, ¿verdad? Del mismo modo, el tipo de salida de un sensor es como un tapón de gasolina: debe adaptarse perfectamente a su sistema de control. En este artículo, le ayudaremos a descifrar el código NPN y PNP y le orientaremos sobre cómo elegir el tipo de salida adecuado para que su equipo industrial funcione sin problemas como una máquina bien engrasada.
Los sensores de proximidad detectan la presencia de objetos cercanos y controlan un interruptor en consecuencia. Suelen tener dos tipos de salida principales: NPN y PNP. En pocas palabras:
| Tipo de salida | Definición | Características de conexión del circuito |
|---|---|---|
| NPN | También llamada salida de hundimiento | La línea de salida se conecta a tierra cuando está activa |
| PNP | También llamada salida de origen | La línea de salida se conecta a la alimentación positiva cuando está activa |
El tipo de salida determina cómo funciona el sensor y cómo se conecta con su sistema de control. Elegir el correcto es el primer paso para garantizar una transmisión precisa de la señal.
Entender en qué se diferencian le ayudará a decidir qué salida se adapta mejor a su aplicación. He aquí una rápida comparación:
| Característica | Salida NPN | Salida PNP |
|---|---|---|
| Conexión de circuitos | Conduce a tierra (negativo) | Conduce a la fuente de alimentación (positivo) |
| Nivel de señal | Nivel bajo (0V) significa activo | Nivel alto (tensión de alimentación) significa activo |
| Entrada del sistema de control | Normalmente recibe la señal de tierra | Normalmente recibe la señal de potencia |
| Regiones comunes | Utilizado principalmente en Asia | Popular en Europa y Norteamérica |
| Inmunidad al ruido | Sensible al ruido de fondo | Mejor inmunidad al ruido |
| NO (Normalmente Abierto) vs NC (Normalmente Cerrado) | Ambos tipos disponibles | Ambos tipos disponibles |
Piense en NPN como el interruptor de "conexión a tierra" del circuito, y en PNP como el interruptor de "conexión a potencia".
Cuando el sensor NPN se activa, la línea de señal va a tierra, y el PLC lee una señal baja como "ON". Para PNP, la activación conecta la línea de señal a la tensión positiva, y el PLC detecta una señal alta como "ON."


Encuentre el sensor de proximidad NPN o PNP perfecto para su sistema. Póngase en contacto con nosotros hoy mismo para recibir asistencia experta.
Su PLC o sistema de control desempeña un papel fundamental en esta elección. Las entradas de control suelen admitir un solo tipo de señal de entrada:
| Entorno de aplicación | Tipo de salida recomendado | Razón |
|---|---|---|
| Industria pesada con motores | PNP | Mejor inmunidad al ruido, señales estables |
| Líneas generales de automatización | NPN | Más controladores admiten entradas NPN |
| Equipos que requieren normas internacionales | PNP | Normas europeas y norteamericanas |
| Sistemas que necesitan protección contra cortocircuitos | En función de las especificaciones | Elija en función de los requisitos de seguridad |
En resumen, evalúe las necesidades de su sistema, las especificaciones del dispositivo y el entorno de trabajo para elegir el mejor tipo de salida. Una combinación adecuada garantiza una recepción fiable de la señal y evita falsos disparos o pérdidas de señal.


Además del tipo de salida, considere:
| Distancia de detección | Aplicación típica | Corriente de salida necesaria |
|---|---|---|
| 1-5 mm | Detección precisa de piezas pequeñas | Baja, adecuada para cargas ligeras |
| 5-20 mm | Automatización industrial general | Medio |
| Más de 20 mm | Equipos grandes o detección a larga distancia | Alta, necesita capacidad de accionamiento estable |
| Tipo de cableado | Características | Casos de uso adecuados |
|---|---|---|
| 2 hilos | Líneas de alimentación y señal compartidas, circuito más sencillo | Usos rentables y sencillos |
| 3 hilos | Líneas separadas de alimentación, señal y tierra | Control más preciso y complejo |
Considérelas junto con las opciones de tipo de salida para obtener un rendimiento óptimo del sensor.
Elegir la salida NPN o PNP adecuada para su sensor de proximidad es vital para una integración perfecta con su sistema de control y un funcionamiento fiable. Comprender sus principios, escenarios de aplicación y diferencias le ayudará a evitar errores de cableado y a mejorar el tiempo de funcionamiento del sistema.
Tanto si es un ingeniero de procesos como un responsable de compras, una elección informada conduce a unos equipos más duraderos y un mantenimiento más sencillo. Si tiene alguna pregunta o necesita sensor de proximidad no dude en ponerse en contacto con nuestros expertos. Estamos aquí para ofrecerle las soluciones de interruptores de proximidad perfectas para su fábrica y su negocio.
No espere más: elija ahora el sensor de proximidad NPN o PNP adecuado y comience su viaje hacia una automatización industrial eficaz y estable.
Si las entradas de su sistema de control se activan por conexión a tierra o su PLC admite señales de tierra, la salida NPN es la elección correcta.
No. Debido a las diferencias en la polaridad de la señal y el cableado, el intercambio sin ajustes puede causar fallos de funcionamiento o daños.
Los interruptores NA cierran el circuito al detectar un objeto; los interruptores NC lo abren. Elija en función de su lógica de control.
Compruebe el manual del dispositivo o consulte al fabricante el tipo de entrada del PLC y el cableado para garantizar la compatibilidad.
No. Muchos PLC sólo admiten un tipo. Compruebe las salidas de sensor compatibles con su modelo de PLC.
En general, no. La velocidad y la precisión dependen más del diseño y la calidad del sensor que del tipo de salida.
Los sensores PNP, debido a su salida de alto nivel, suelen ser más fáciles de detectar en caso de avería, lo que los hace ligeramente más seguros.
Siga siempre atentamente las instrucciones de cableado. Utilice cables y conectores claramente marcados para evitar errores de conexión.