Explosion Proof Pendant Control Station with Certifications and Features
Explore explosion proof pendant control stations with certified safety, durable enclosures, multiple button options, and customization for hazardous areas.
Lire la suite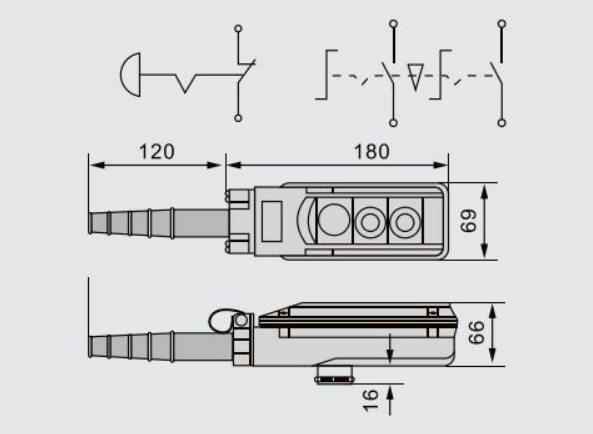

In today’s fast-paced industrial environment, safety and efficiency are really important. Télécommande de pont roulant systems have become one of the most valuable tools for industries—whether it’s manufacturing, construction, or logistics. They allow operators to control cranes from a safe distance, offering better visibility and increasing productivity.
In this guide, we’ll explore the basic structure and key components of overhead crane remote controls. If you’re thinking about upgrading your crane operations or simply want to understand how these systems work, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive into the core parts that make up these advanced control systems, and how they work together to ensure your operations are safe, precise, and efficient.
A typical overhead crane remote control COB-61 setup comprises several key components working seamlessly through wireless technology. At its core, it’s about communication between a transmitter (the remote held by the operator) and a receiver (mounted on the crane). Here’s a simplified overview:
| Composant | Fonction |
|---|---|
| Émetteur | Portable device with buttons or joysticks for inputting commands. |
| Récepteur | Mounted on the crane, receives signals, and controls crane motors. |
| Control Circuit | Manages signals, ensuring accurate operation, safety, and synchronization. |
| Power Supply | Batteries for transmitters, electrical power for receivers. |
Each part plays an essential role in ensuring smooth, safe crane operation. But what makes modern remote controls truly effective are their advanced features designed to improve safety and functionality. Let’s look closer at each of these parts and explore how they work together during operation.
Would you like to see a detailed breakdown of each part’s function or specifics on how wireless communication works?


The transmitter is the handheld device your operators use daily. It usually comes with
Some transmitters are designed with rugged materials for industrial environments, featuring ergonomic layouts for comfort during long shifts. Advanced models also include feedback features such as LED indicators or small screens showing load status or system warnings.
Mounted directly on the crane, the receiver is the system’s brain. It interprets signals from the transmitter, activating motor controls and safety features accordingly.
| Part | Fonction |
|---|---|
| Signal Decoder | Interprets radio signals received from the transmitter. |
| Motor Controllers | Drive the crane’s hoists, trolleys, and bridge movements. |
| Safety Interlocks | Prevent unsafe movements or operations. |
Many modern systems integrate microprocessors and encryption, ensuring that only authorized controllers can operate the crane, defending against interference or hacking.
| Dispositif de sécurité | Objectif |
|---|---|
| Saut de fréquence automatique | Avoids interference from other RF devices. |
| Cryptage | Protects against unauthorized control. |
| Arrêt d'urgence | Instantly halts all crane movements if needed. |
| Link Monitoring | Ensures ongoing communication; triggers shutdown if the connection drops. |
Battery life and power stability are critical. High-quality systems incorporate low-battery alerts and robust power management, reducing downtime and ensuring consistent operation.


Upgrade your crane operations with our reliable overhead crane remote controls. Boost safety and productivity with wireless crane control systems designed for industrial efficiency.
Modern overhead crane remote controls are not just about simple start/stop functions. They often include:
Example of the control system layout
| Module | Description |
|---|---|
| Joystick | Multi-axis movements for precise control |
| Buttons | Specific commands like hook locking, auxiliary functions |
| Display | Real-time data on load, system status |
| Safety Exit keys | Quickly disable operations in emergencies |
In essence, these added functionalities help operators perform complex tasks with confidence, reduce risks, and elevate safety standards.
In summary, overhead crane remote control systems are a vital part of modern industrial operations. Their core components—transmitter, receiver, control circuitry, and power supply—work together to deliver safe, precise, and efficient control over heavy lifting tasks. As technology advances, these systems are becoming smarter, more reliable, and user-friendly, paving the way for safer workplaces and higher productivity.
Whether you operate in manufacturing, construction, or logistics, understanding these basic structures and parts helps you make informed decisions when selecting or maintaining remote controls. Ready to enhance your crane operations? Dive into today’s market options or contact us for customized solutions—your safety and efficiency are worth it.
It uses wireless radio frequency signals sent from the handheld transmitter to the mounted receiver, which then activates crane motors.
Most systems operate reliably within 100–200 meters, some advanced models like the Panther system can reach up to 1,600 feet.
Features include encrypted signals, automatic frequency hopping, emergency stop buttons, and link monitoring for constant connection checks.
Yes, many modern systems support multi-crane operation with synchronized controls.
They are designed to withstand vibration, dust, temperature extremes, and other tough conditions.
Regular battery checks, software updates, and safety inspections are recommended to keep systems operating smoothly.