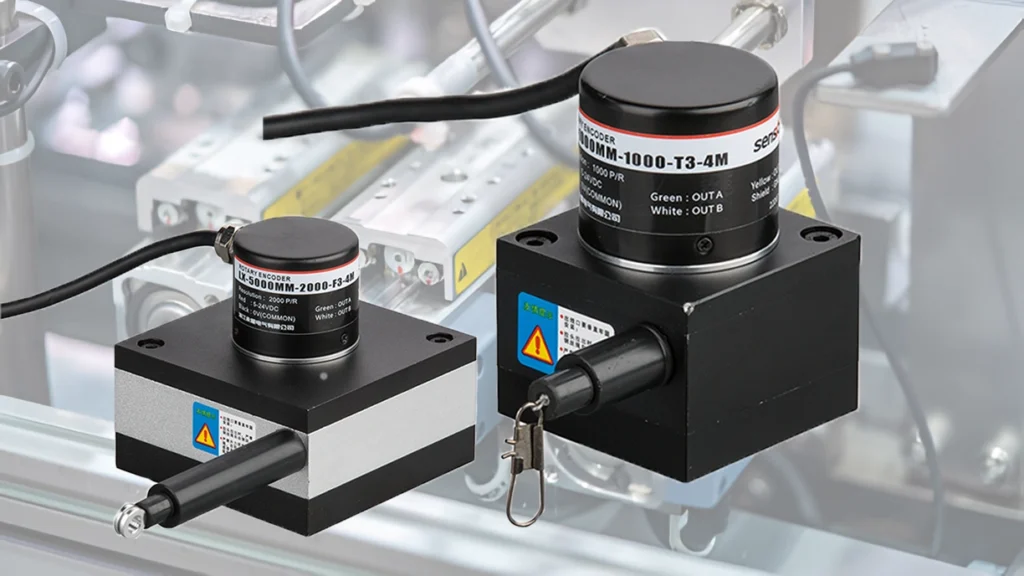
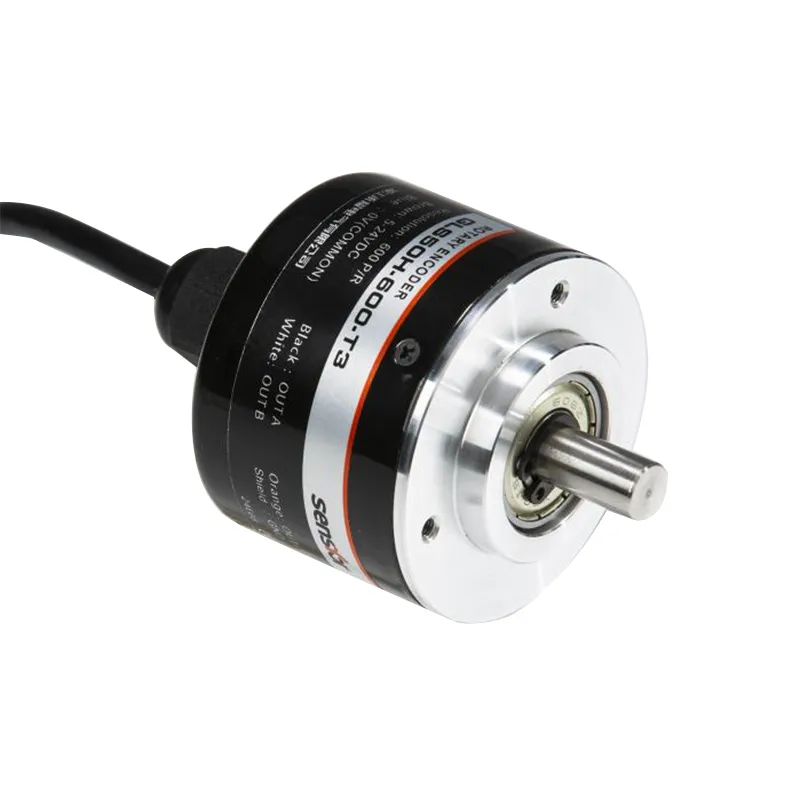
Incremental Rotary Encoder High Precision A B Z Signals
Incremental rotary encoders are cost-effective sensors designed to measure relative position, speed, and direction in various industrial applications. They provide quadrature A/B signals and optional index/Z pulses, enabling precise motion feedback and control. Wilmall incremental rotary encoders stand out for their: Feature Details Resolution Range 100 to 10,000+ PPR/CPR Output Signals Quadrature A/B, optional Index/Z pulse Output Types TTL, HTL, RS-422, Open Collector, Push-Pull Shaft Options Ø6mm, Ø8mm, Ø10mm solid; hollow shaft types Supply Voltage 5V, 5-24V, 10-30V DC Protection Ratings IP50 to IP67 for dust and water resistance Wilmall’s incremental rotary encoders provide reliable, accurate speed feedback and relative position sensing, meeting the demands of automation, robotics, and motor […]
続きを読む